- Supercool
- Posts
- 🌐 Apple-ifying Energy: Renew Home Makes Virtual Power Plants Painless & Profitable
🌐 Apple-ifying Energy: Renew Home Makes Virtual Power Plants Painless & Profitable
Building the energy layer that’s everywhere and nowhere at once.
To make the clean energy transition work, we must stop asking people to care about energy—and start designing systems that keep rewarding them just for signing up.
That’s Renew Home’s bet.
Formed in 2024 through the merger of two home energy management heavyweights—Google’s Nest Renew and OhmConnect—Renew Home is building an energy layer that’s everywhere and nowhere at once.
Their software integrates into devices people already own—smart thermostats, EV chargers, water heaters—and connects them to the grid. No behavior change. Just automation, comfort, and financial rewards.
And this layer is not theoretical. It’s already delivering measurable benefits to 5 million U.S. households, the utilities that serve them, and the climate.
The company’s roots give it a head start. Its software powers every Nest Thermostat. Yup, the smart, good-looking one. The one designed by famed Apple designer Tony Fadell. The one with a 27% market share of the smart thermostat market.

The Nest Renew Thermostat now has added intelligence powered by Renew Home.
Fifteen years into the journey, this is just the beginning.
“Our goal is to make participating in energy programs as easy and rewarding as possible for homeowners—ideally, they don't even have to think about it,” says Jeff Gleeson, Chief Product Officer at Renew Home.
Jeff joined me on the Supercool podcast this week to walk through how his team makes Virtual Power Plants functional and, ideally, irresistible.
But Virtual Power Plants Need a Rebrand
If you’re not in the energy world, Virtual Power Plant (VPP) probably sounds like a buzzword born in a windowless conference room. Even if you are, it still might.
That’s a problem—because VPPs are critical to our low-carbon future.
As energy demand surges—from climate extremes, electrification, and AI—our aging grid faces more stress than ever.
As Grid Strategies, a highly respected consultancy, stated: “The era of flat energy demand is over.”
Forecasts now project U.S. grid power demand to rise 16% over the next five years.
That’s massive.
Traditional power plants take years to build—and many still burn fossil fuels. But VPPs are different.
They reduce demand not by flipping off the lights but by shifting when devices use electricity: a thermostat pre-cools your home by a degree. A water heater delays running for 30 minutes. An EV charger pauses during peak hours. And they tune themselves to run when more clean energy is on the grid. All of these modifications are imperceptible. No sacrifice.
Multiply that across hundreds of thousands of households, and you’re at power plant scale—without spending hundreds of millions on power plant equipment and more on new transmission lines.
That simple equation adds up to a 21st-century gold rush. It’s what led the U.S. DOE to update its Virtual Power Plant Liftoff Report early in January, just weeks before the clean energy brain trust appointed by Biden left town.
The opportunity grows as more of these devices (e.g., distributed energy resources, or DERs) are deployed in homes. Combined, the devices that fold into VPPs are forecast to grow nearly as fast as new energy generation.
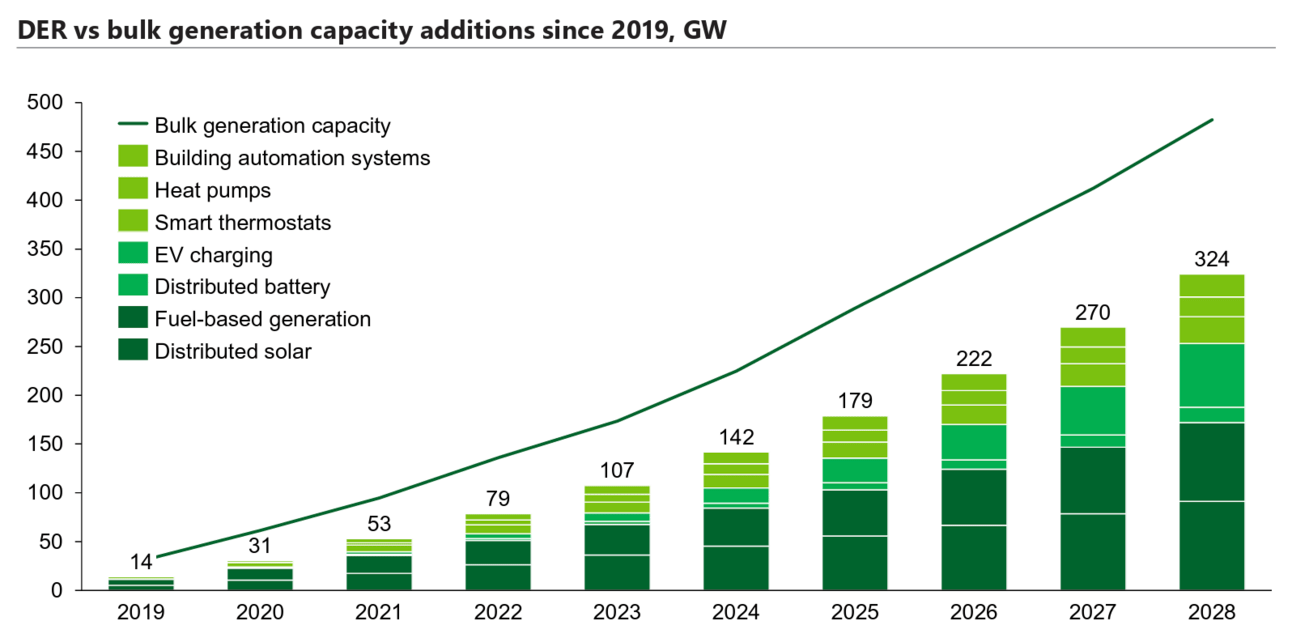
Source: U.S. DOE VPP Liftoff Report with data from Wood Mckenzie
It’s not just Renew Home that has its eye on the prize.
We’ve spotlighted other contenders, like Mary Powell, CEO of Sunrun (episode 33), the nation’s largest home solar and battery storage company, and Dan Lotano, COO of GridLeap (episode 31), the nation’s largest financier of home solar systems. Both companies are leveraging their customer relationships to grow VPPs.
Still, convincing people to participate is challenging for all of these companies. And that’s a marketing problem.
“Terms like ‘Virtual Power Plant’ don’t resonate with the average person,” Jeff says. “We focus on communicating benefits like savings and comfort in straightforward, relatable language.”
Comfort. Simplicity. Money. That’s the messaging stack that nudges people from yawn to yes.
You Can’t Shout at the Grid and Expect It to Change
Most energy efficiency programs ask too much of people.
“Change your habits.”
“Check the app daily.”
“Mind your TOU (Time of Use) window.”
No one wants to live like that. Renew Home knows it. Jeff and many of his colleagues have been in this world for over a decade. They’re energy nerds. They love this stuff.
But at some point, Jeff hit a realization that changed his approach.
"It took me a while to accept that not everyone is as excited about energy as I am."
So, they designed a system that asks less and delivers more.
“We’ve learned you can’t rely on people to constantly engage with energy,” Jeff says. “It needs to run in the background—automated, intuitive, and non-intrusive.”
Why Utilities Are Suddenly Paying Attention
For years, utilities saw residential demand response as too small, inconsistent, and messy to matter.
Not anymore.
Between weather extremes and data center booms, grid operators are under pressure.
“Utilities are increasingly recognizing the value of residential demand flexibility,” Jeff says. “They see how it can support reliability and decarbonization goals without major infrastructure investments.”
Renew Home’s deep experience in the utility industry makes it a trusted partner. They know how to navigate program design, incentive structures, and regulatory constraints.
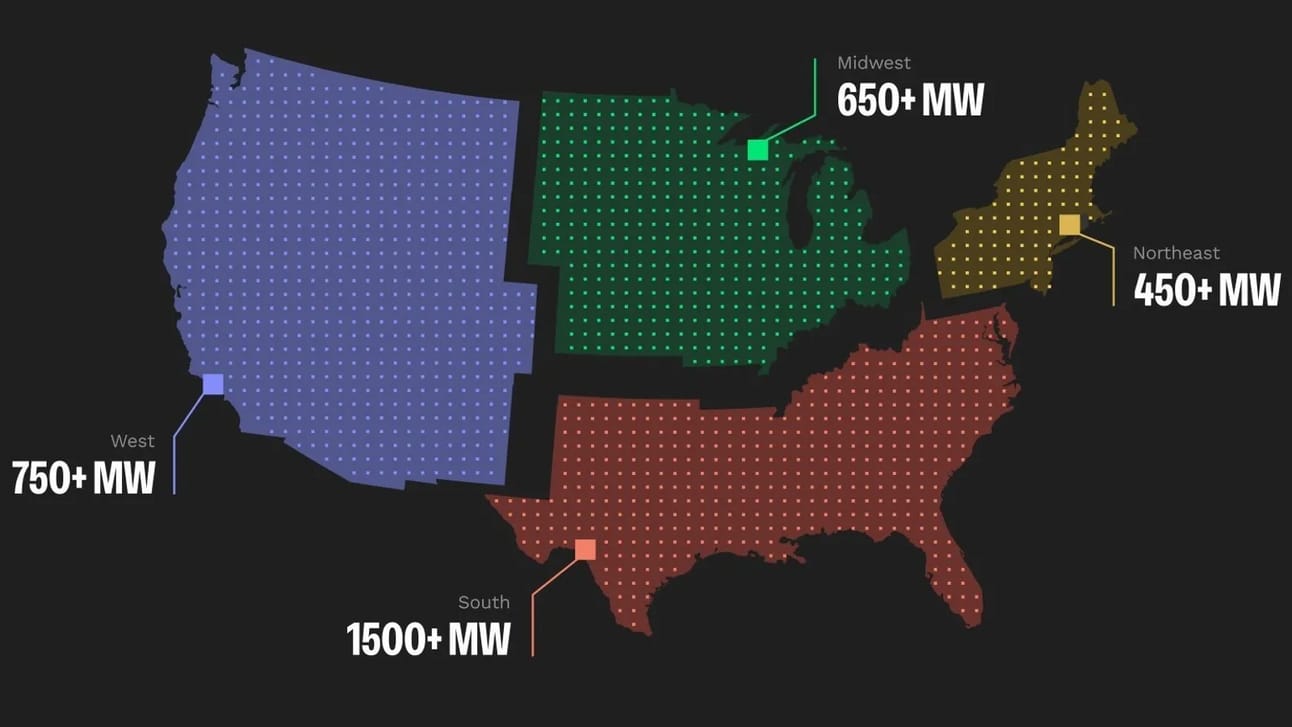
U.S. footprint of power load that Renew Home controls.
Across the U.S., partnerships with over 100 energy providers enable Renew Home to manage 3 GW of shiftable household load.
Now, the company is leveraging its market positioning to roll out more advanced VPP features for energy providers, starting this summer.
Smart Thermostats Were Just the Beginning
Fifteen years ago, smart thermostats promised to learn your habits and lower your bills. And they delivered. But they weren’t solving the big problem.
They were gadgets—not grid tools.
Today, that’s changing. Thermostats—and other connected devices—are becoming critical infrastructure. They’re influencing when and how electricity flows across the country.
And Renew Home is the connective layer.
“We’re not a hardware company,” Jeff explains. “We’re the software layer—the intelligence that sits inside those devices and turns them into grid assets.”
That strategy gives Renew Home a clear advantage. They don’t need to manufacture or install anything. Their platform simply rides the wave of devices already entering people’s homes—driven by electrification, decarbonization, and smarter living.
They plug in. They optimize. They scale.
Supercool Takeaway
The most important power plants in a low-carbon economy might be the ones that never get built.
If you can avoid peak demand spikes, you don’t need natural gas peaker plants—that fire up during peak energy hours.
If you can shift flexible loads across homes, you don’t need a new substation.
If your software makes decarbonization feel effortless for households and empowering for utilities, you’ve accelerated the low-carbon economy.
That’s Renew Home’s strategy. It’s not loud or flashy. It’s invisible, integrated, and effective.
For the price of a smart thermostat, it’s coming to your neighborhood and likely your home.
Listen to this podcast episode on Apple, Spotify, YouTube, and all other platforms.

↓
Stat of the week: 60%
That’s the cost-benefit of scaling a virtual power plant for a utility compared to a natural gas peaker plant, according to Ben Brown, Renew Home’s CEO. Virtual power plants can provide the same dispatchable capacity for 60% of the cost.
Quote of the week:
“Frankly, it is the only way for them to integrate all of the huge load that is coming their way.”
—Jigar Shah, Former Director of Loan Programs at the U.S. Department of Energy, on why utility companies must adopt virtual power plants.
↓
Virtual Power Plants are catching fire across the globe. I linked to a couple of episodes above that we’ve done with other industry players. But this is the early innings of a trend we’re going to hear more about.
Here are a few other developments worth keeping an eye on.
Base: Building A Distributed Backup Battery Network
In Texas, Base is scaling a new kind of Virtual Power Plant built from residential backup batteries. For as little as $495 upfront, homeowners obtain whole-home battery storage that kicks in during outages and supports the grid during peak demand. Base installs and manages the systems, using them as distributed energy assets while giving households peace of mind and lower energy bills.
The company, led by Zach Dell (Michael Dell’s son), just raised a $200 million Series B round to accelerate growth.
MCE: Expanding VPP Benefits Across Communities
In California, MCE, a nonprofit public agency with a mandate to deploy renewables at competitive rates, is expanding equitable access to the benefits of Virtual Power Plants. Richmond residents in its new program receive free or low-cost energy appliances and upgrades and let their devices support the grid during peak times—earning bill credits and cutting emissions.
China: Going GigaWatt Scale for VPPs
In Jiangsu Province, Jiangsu Electric Power is building what may be the world’s largest Virtual Power Plant. For me, it’s personal—I moved to Nanjing, the province’s capital, in 1995. Back then, the energy landscape was a different story. No VPPs. No winter heat. The Chinese Communist Party had declared all cities south of the Yangtze River “warm.” Many were. Nanjing wasn’t. So I wore longjohns from November to May.
Oh, how things have changed.
Supercool in the Pods-Sphere
I’ve been a guest on several recent podcasts to discuss Supercool climate solutions, Plantd (the carbon-negative building materials company I co-founded), and the trends accelerating the low-carbon economy.
Grid Connections: Josh Dorfman on Carbon-Negative Building Materials
Sea Change Radio: Josh Dorfman Supercool Building Materials
↓
Not yet subscribed to Supercool?
Click the button below for weekly updates on real-world climate solutions that cut carbon, boost the bottom line, and improve modern life.
🌐