- Supercool
- Posts
- 🌐 Cleaning the Grid: Wärtsilä Tackles the Toughest Battery Storage Projects on Earth
🌐 Cleaning the Grid: Wärtsilä Tackles the Toughest Battery Storage Projects on Earth
Grid-scale batteries are the fastest-growing energy tech on the planet.
Ask someone deep in the industry about grid-scale battery storage, and they’ll tell you: the best sites are already gone.
Taken. Already operational.
It’s a striking indicator of how rapidly utility-sized batteries are scaling worldwide.
That’s what Dave Hebert, VP of Global Sales & Business Strategy at Wärtsilä for its Battery Storage division, told me has already happened in Australia.
Batteries—largely the same lithium-ion chemistry in your phone, only thousands and thousands of them now deployed on sites that span the lengths of football fields, across Australia, Europe, the U.S., and China. Nearly everywhere.
The global clean energy revolution is underway. And let’s be clear: it is global, and it is a revolution.
Last week, I wrote about how global clean energy investment is on track to surpass $2 trillion for the second consecutive year, nearly doubling fossil fuels. For context, fossil fuels have never attracted $2 trillion of annual investment.
We are in a new age of adoption, as Keith Zakheim, CEO of Antenna Group, has coined it. And grid-scale battery storage is now the fastest-growing energy technology on the planet. Prices are dropping and deployments are booming.
📈 Global capacity is expected to hit 80 GW this year—8x more than 2021, 80x more than a decade ago.
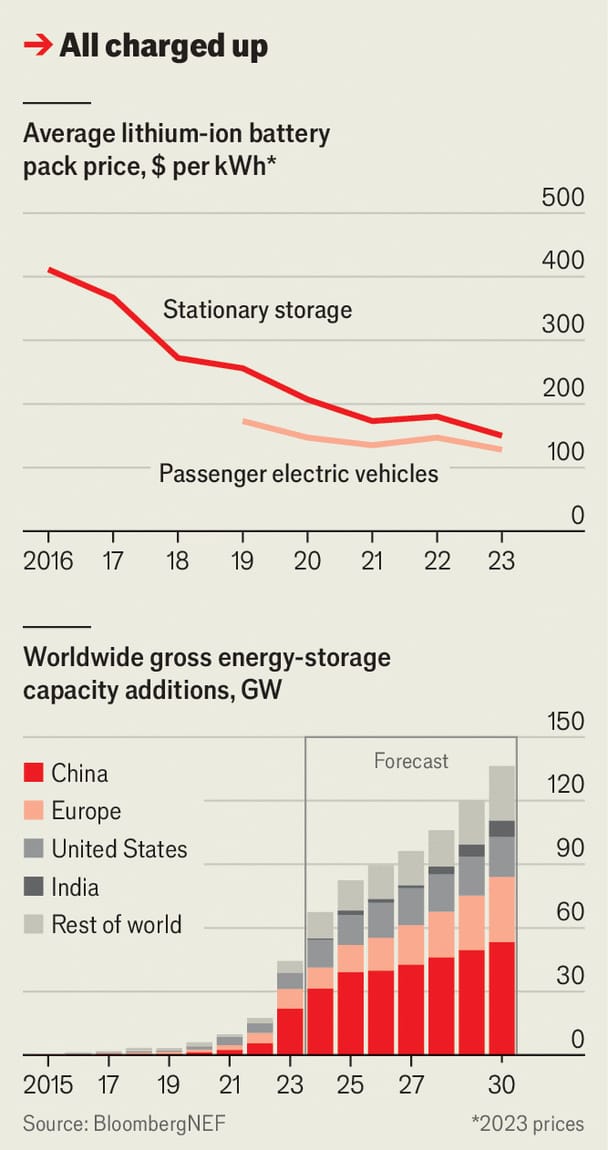
For most of us, this revolution is invisible, happening at the edge (to use the industry’s lingo), in deserts, on top of mountain ranges, or out at sea— places often far removed from population centers.
But the surge is undeniable, and at its center are grid-scale batteries.
⚡ Makes solar and wind energy dependable
🚗 Cushions and absorbs shocks from an increasingly electrified world
🛠️ Stabilizes aging 20th-century grid infrastructure
Wärtsilä is leading this growth.
Wärtsilä’s Global Impact
Headquartered in Finland with a 180-year history, Wärtsilä is a global leader in energy storage, power generation, and maritime propulsion, operating in 180 countries.
Tens of thousands of ships rely on Wärtsilä’s engines, hybrid systems, and decarbonization tech to keep them running cleanly. In terms of raw power generation, it’s deployed 79 GW of installed global capacity. And when it comes to batteries, the company has deployed or contracted over 17 gigawatt-hours of grid battery storage across more than 130 sites worldwide—enough to power millions of homes.
When it comes to working with customers, the company has an affinity for first-of-its-kind technologies. Doing the technically hard stuff to push the clean energy transition forward.
That means supplying the electric propulsion system for the first battery-electric, zero-emission high-speed passenger ferries, soon to be deployed in San Francisco. And developing modular hybrid engines for large container ships that start with LNG, pair with renewables, and scale to hydrogen.
Battery Storage in Scotland: First-of-its-kind on the Grid
A case in point: Blackhillock
Working with clean energy partner Zenobē in Scotland, Wärtsilä deployed Europe’s largest battery storage system, the first to utilize advanced power electronics, enabling higher uptake of renewable energy onto the grid.

Blackhillock, where Wärtsilä’s batteries are operational.
That system:
🔋 Absorbs excess wind power from three major offshore farms, capturing clean energy that would otherwise go to waste.
⚡ Provides advanced grid stability services, like synthetic inertia and short-circuit power, traditionally delivered by fossil fuel plants.
💸 Cuts consumer costs and emissions—expected to save UK households an estimated £170 million and avoid 2.6 million tonnes of CO₂ over 15 years.
“This is what Wärtsilä does best,” Dave says. “We bring innovation from every corner of our business—whether it’s ships or storage—and make it work for the world.”

Beatrice, a 588MW wind farm off the coast of northern Scotland, is one of three major wind installations connected to Blackhillock.
A similar mindset powers Wärtsilä’s grid-scale batteries in Texas, California, and Hawaii.
Supercomputers at the Edge
Batteries are straightforward. What sets Wärtsilä apart is its software. And that’s GEMS, a proprietary digital management platform that monitors every battery cell in real-time, squeezing out maximum performance across the whole system.
“We put supercomputers out on the edge to control these systems in real time,” Dave says. “We have more cloud data transfers than Twitter does. We’re managing massive amounts of data to optimize performance in ways no one else is doing.”
The software ensures every cell is working perfectly and predicts issues before they happen. GEMS makes the system smarter, faster, and more reliable, transforming raw data into immediate action and maintaining optimal efficiency.
It’s not just about big batteries—it’s about making them work better.
Noise and Fire: The Next Frontiers
As battery storage moves closer to cities, noise and fire safety challenges are heightened. Wärtsilä already contends with seismic risks and cybersecurity. Now the concerns are as technical as they are human.
“Now everything has a noise problem,” Dave explains. “We’re getting closer to population centers. With solar and wind, people try to stop them by saying they don’t want to see them. With batteries? No one wants to hear them. Or rather, all the components that keep them cool.”
Wärtsilä focuses on innovative cooling systems and noise-reduction techniques, like designing enclosures that keep things quiet.
“Whether it’s noise reduction or fire suppression, we’re solving the problems others don’t think about,” Dave says. “We make sure our systems fit into cities without friction.”
Mission: Impossible
As Dave and I spoke, images of Ethan Hunt sprang to mind. One minute, Dave and his team are working to deploy mission-critical infrastructure that keeps civilization going. The next, he’s back home mowing the lawn and trotting down to the grocery store to grab some more ice (that would be Mission: Impossible 4— Ghost Protocol).
Those closest to him don’t know exactly what he does when he’s gone.
“My family still thinks I sell solar modules. I’ve never sold solar modules,” said Dave.
Wärtsilä’s work is like that. The projects are high-stakes, requiring focus, precision, and the ability to innovate on the fly.
“We like projects that are technologically hard, logistically hard—when it’s off-island and will help the grid wind down with wind power after the DC couple to the main island shuts off. Where we’re controlling the entire grid or doing all these innovative services out on the cutting edge—synthetic inertia, active voltage regulation, very fast, hundreds of milliseconds response.”
Yup, Mission: Impossible.
What Does All This Grid Storage Mean?
Wärtsilä’s systems power three key shifts that the clean energy transition relies on.
⚡ More renewables: Batteries don’t just store energy—they ensure renewable energy is always available.
▦ Grid stabilization: Like an airbag for the grid, batteries smooth out the peaks and valleys, keeping everything running smoothly when demand or generation spikes.
🔋 Grid modernization: Batteries help old infrastructure keep up with electrification’s demands—and can deploy cheaper and faster than fossil fuel plants.
Supercool Takeaway
The clean energy transition doesn’t need to be perfect. And it doesn’t have to wait for ideal conditions.
Wärtsilä demonstrates how blending ambition and fearlessness with precision and practicality can lead us toward a low-carbon future.
Welcome to the age of batteries, coming ever closer to a town near you.
Listen to this podcast episode on Apple, Spotify, YouTube, and all other platforms.
↓
This Week’s Supercool Sponsor

Built to last. Designed to inspire.
Mill is sleek, sculptural, and capable of exerting 288 lbs of force. Each food recycler is crafted by hand in North America and engineered by leaders from Apple and Nest.
Mill transforms your uneaten food into nutrient-rich food grounds and compost, for use at home and in your community.
Buy, finance, or rent your Mill Food Recycler.
↓
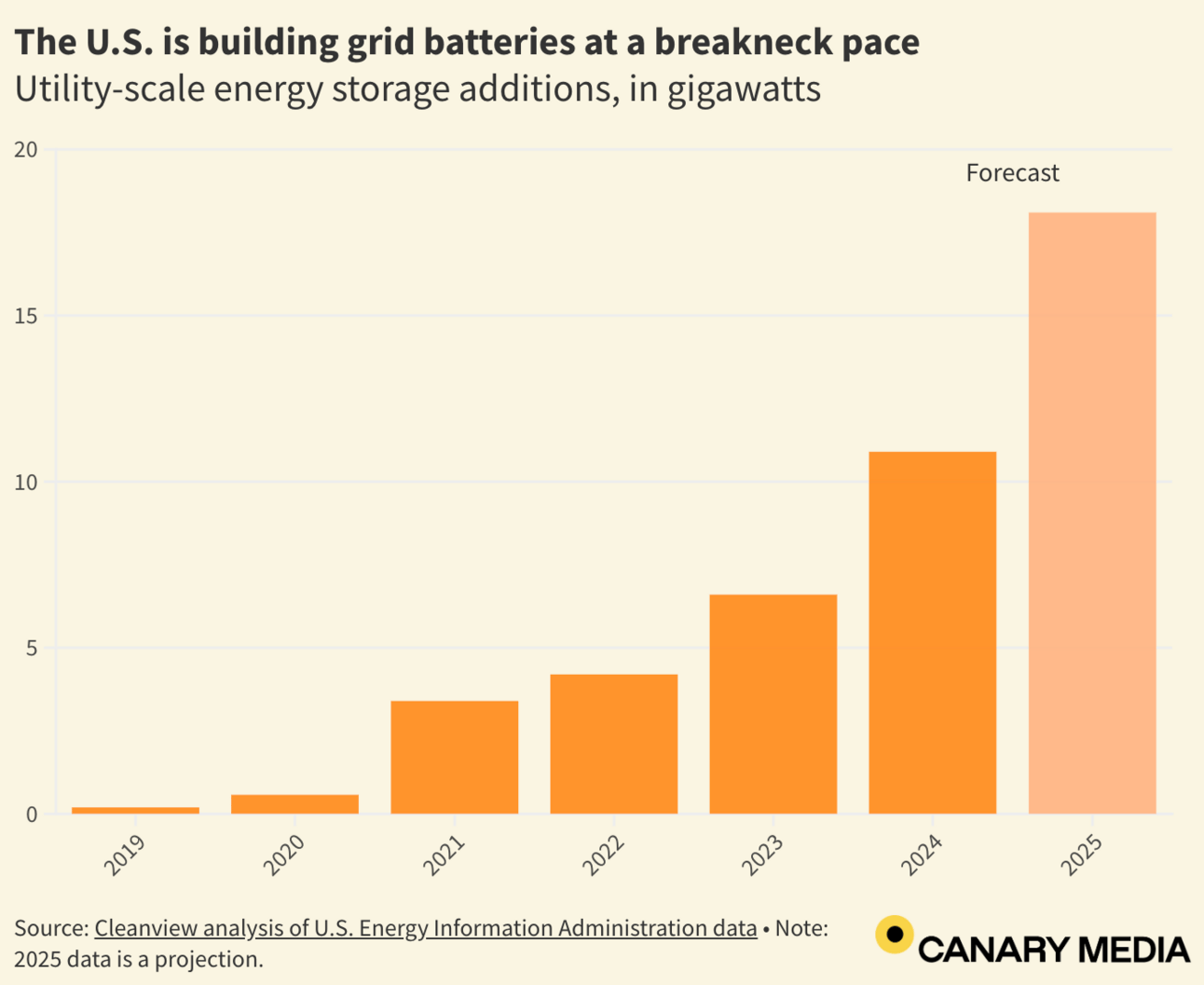
Stat of the Week: 11 GW
In 2024, the U.S. installed 11 gigawatts of new utility-scale energy storage capacity, a figure projected to rise to 18 gigawatts this year (despite pending legislation in Washington, D.C). Source: Canary Media
Quote of the Week:
We know where we want to go, but all those steps on the road need to be carefully planned and carefully crafted. We have a saying in Wärtsilä that ‘green is not black or white’ — there is no single simple solution to the transition.
↓
As the U.S. eyes the next wave of grid modernization, domestic energy storage production is rapidly expanding.
In April, a coalition of companies announced a $100 billion investment to develop and buy grid batteries in the U.S. “We’re investing to ensure that in five years, every part of the energy storage industry is anchored here in America,” said Jason Grumet, CEO of American Clean Power (ACP).
Here’s who's out in front:
Tesla is expanding its Nevada Gigafactory, increasing production to meet the surging demand for grid-scale batteries. Globally, deployments of its Powerwall and Megapack doubled in 2024 to 31 GWh.
Fluence is opening a new manufacturing site in Goodyear, Arizona, producing essential components like battery management systems and enclosures for large-scale storage solutions.
LG Energy Solution is ramping up U.S. production with a new plant in Michigan, ensuring domestic sourcing of clean energy storage.
Form Energy is transforming a former steel mill site in West Virginia into a cutting-edge battery manufacturing hub, advancing long-duration storage technology crucial for grid stability.
The project has garnered widespread support.
"We need clean power, we need more power, and we need the ability to store power," said West Virginia Senator Shelley Moore Capito.
We’ll leave it with this: from the Senator’s lips to her colleague’s ears.
↓
Not yet subscribed to Supercool?
Click the button below for weekly updates on real-world climate solutions that cut carbon, boost the bottom line, and improve modern life.
🌐
